Warehouse Location Coding – A Critical Enabler of Operational Excellence
Introduction to Warehouse Location Coding
Warehouse operations may look simple from the outside—receive goods, store them, pick them, and ship them. But behind the scenes, it’s a carefully choreographed dance. One wrong step, and everything slows down. This is where warehouse location coding comes in.
What Is Warehouse Location Coding?
Warehouse location coding is a structured system used to assign a unique “address” to every storage position in a warehouse. Think of it like a GPS for your inventory. Instead of guessing where a pallet is, you know exactly where to go—every time.
Why It’s More Than Just Labels
This isn’t about sticking random stickers on racks. A well-designed location code creates a shared operational language between people, equipment, and systems. When done right, it becomes the backbone of warehouse efficiency.
The Role of Location Coding in Modern Warehousing
From Manual Warehouses to Smart Warehouses
In traditional warehouses, operators relied on memory and experience. That might work for small operations, but it collapses under scale. Modern warehouses demand speed, accuracy, and real-time data—none of which are possible without structured location coding.
Location Coding as an Operational Language
A warehouse location code speaks to everyone: forklift drivers, pickers, supervisors, and WMS systems. It removes interpretation and replaces it with clarity.
Understanding a Standardized Warehouse Location Code
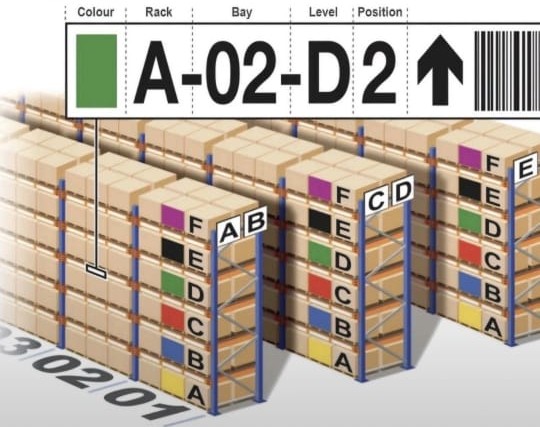
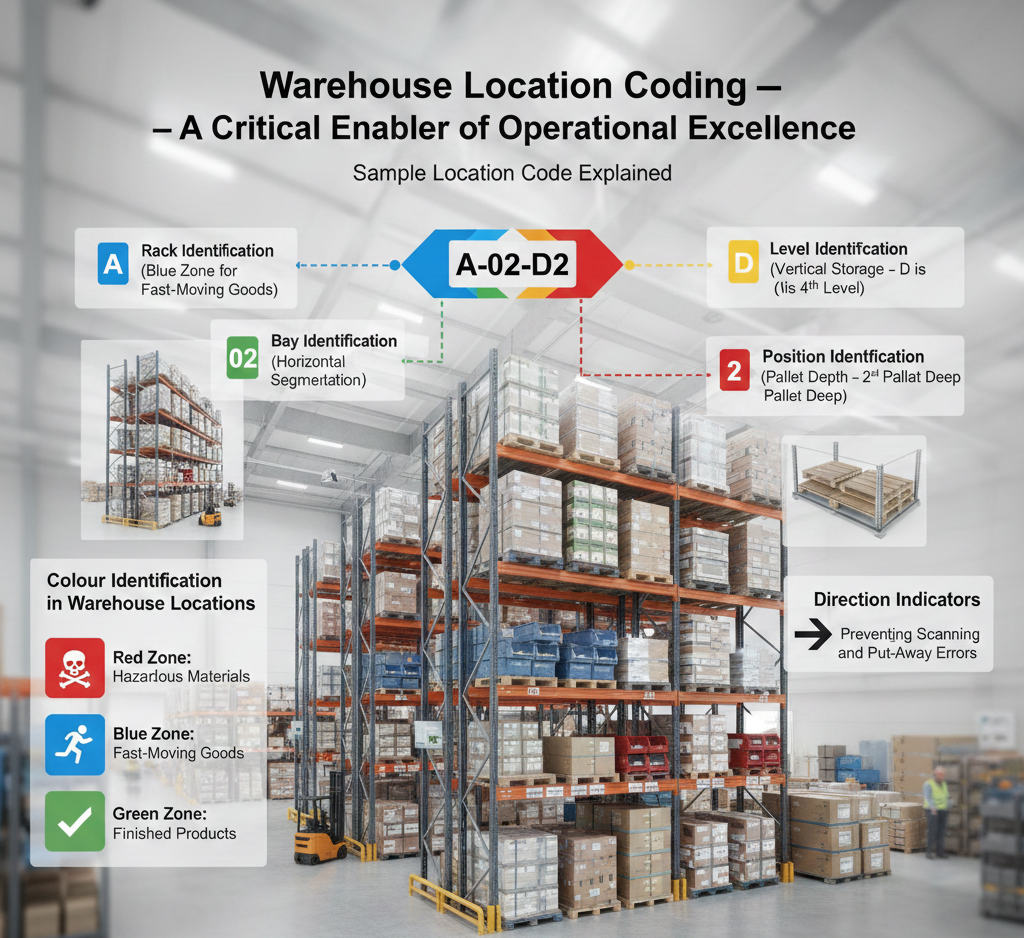
Sample Location Code Explained: A-02-D2
Let’s break down a standardized example:
A-02-D2
Each character has a purpose. Nothing is random, and nothing is optional.
How Standardization Eliminates Ambiguity
Standardization ensures that “A-02-D2” means the same thing to every operator, shift, and system. No confusion. No assumptions. Just precision.
Colour Identification in Warehouse Locations
Purpose of Colour Coding
Colour identification is a powerful visual tool. It helps operators instantly recognize zones, storage conditions, or product categories without reading a single label.
Practical Examples of Colour-Based Zoning
- Red zones for hazardous materials
- Blue zones for fast-moving goods
- Green zones for finished products
It’s like traffic lights—your brain processes colour faster than text.
Rack Identification (A)
Importance of Rack and Aisle Coding
The rack or aisle identifier is the backbone of the location system. It defines the warehouse’s physical structure and ensures logical navigation.
Supporting Warehouse Layout Logic
Clear rack coding aligns with layout planning, making expansion and reconfiguration far easier down the road.
Bay Identification (02)
Horizontal Segmentation Explained
Bays divide racks horizontally. This allows precise positioning and eliminates “close enough” storage decisions.
Travel Optimization for Operators
Well-structured bay numbering minimizes walking and driving distances, saving time and energy on every task.
Level Identification (D)
Vertical Storage Levels and Safety
Levels usually run from A (lowest) to F (highest). This matters more than you think—especially for load weight and equipment limitations.
Impact on Picking Strategies
Fast-moving items can be stored at ergonomic levels, reducing fatigue and improving picking speed.
Position Identification (2)
Pallet Depth and Slot Accuracy
Position numbers define exact pallet depth. No more guessing whether a pallet is in front or behind another.
Avoiding Misplacement and Loss
Clear position coding prevents double-stacking errors and lost inventory.
Direction Indicators in Warehouse Locations
Why Direction Matters
Direction indicators clarify rack orientation. This is critical for scanning accuracy and correct put-away.
Preventing Scanning and Put-Away Errors
A simple arrow can save hours of rework and investigation.